Effective Price Floor A Surplus

Rectangles a and d.
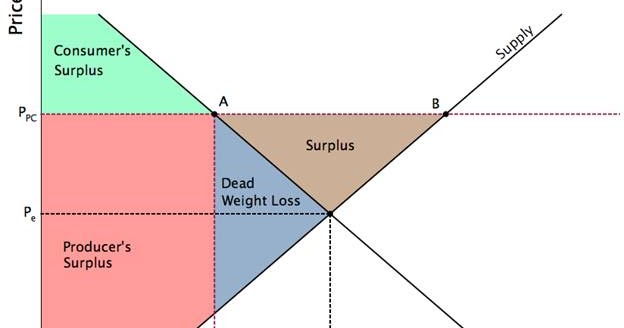
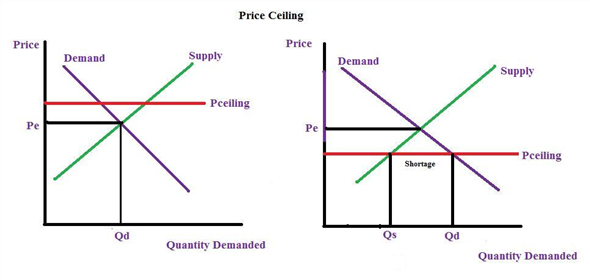
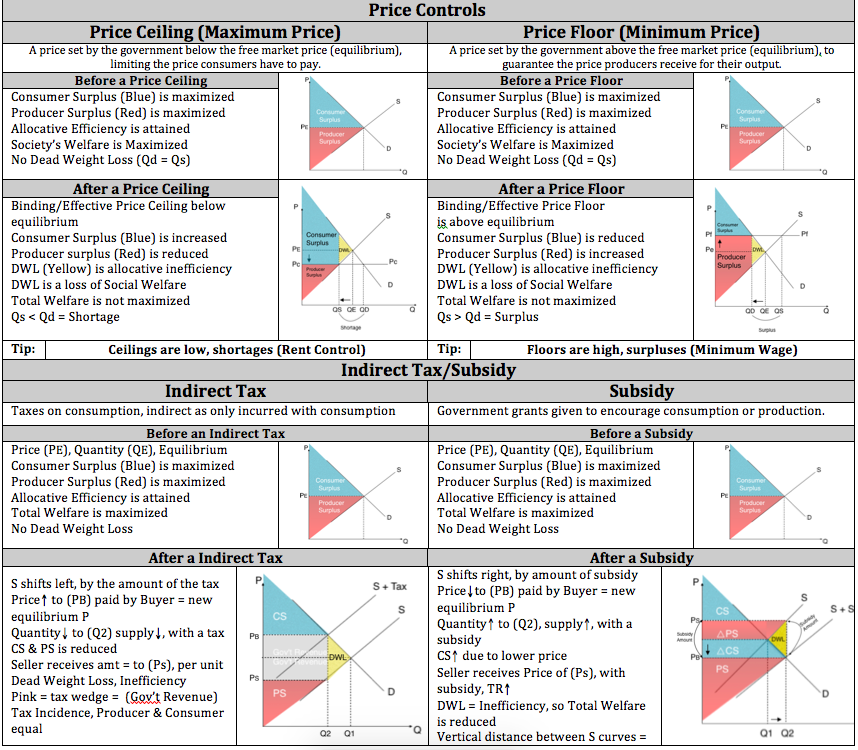
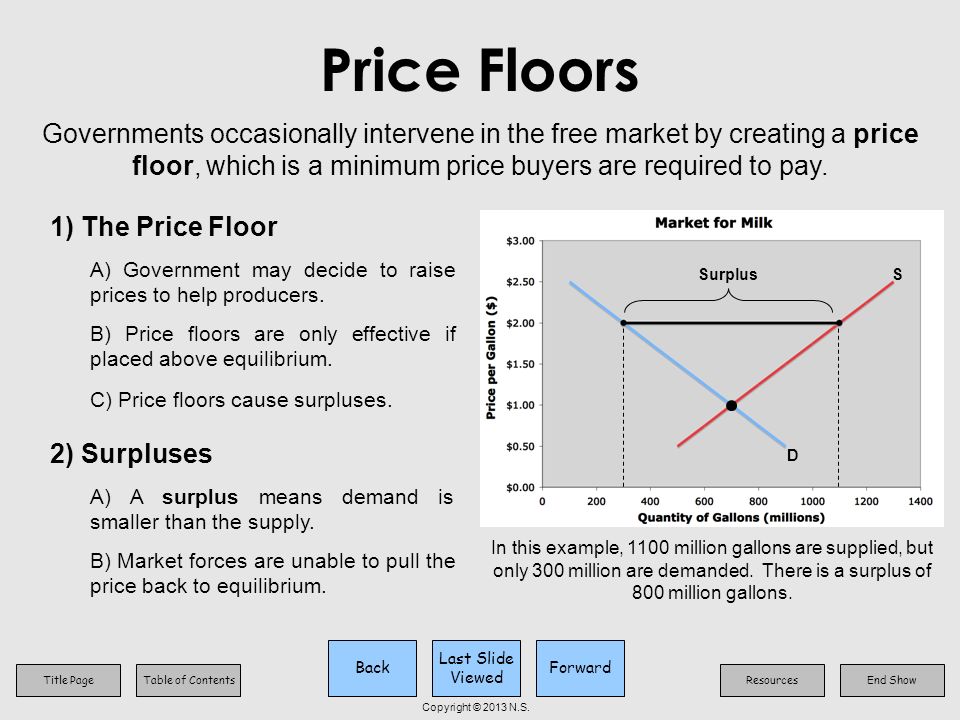
Effective price floor a surplus. Example breaking down tax incidence. A mandated minimum price for a product in a market. Suppose a price is imposed on eggs above their equilibrium price. The most common example of a price floor is the minimum wage.
The likely result will be. Legislating a minimum wage is commonly seen as an effective way of giving raises to low wage workers. For a price floor to be effective the minimum price has to be higher than the equilibrium price. A good example of how price floors can harm the very people who are supposed to be helped by undermining economic cooperation is the minimum wage.
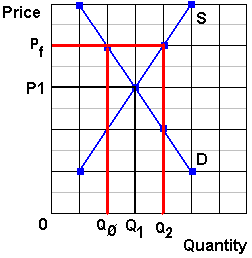
Rectangle b and triangle e. With an effective price floor at pf total surplus is reduced by. Implementing a price floor. Refer to the graph shown.
The effect of government interventions on surplus. For example many governments intervene by establishing price floors to ensure that farmers make enough money by guaranteeing a minimum price that their goods can be sold for. An effective price floor at pf causes consumer surplus to. Price ceilings and price floors.
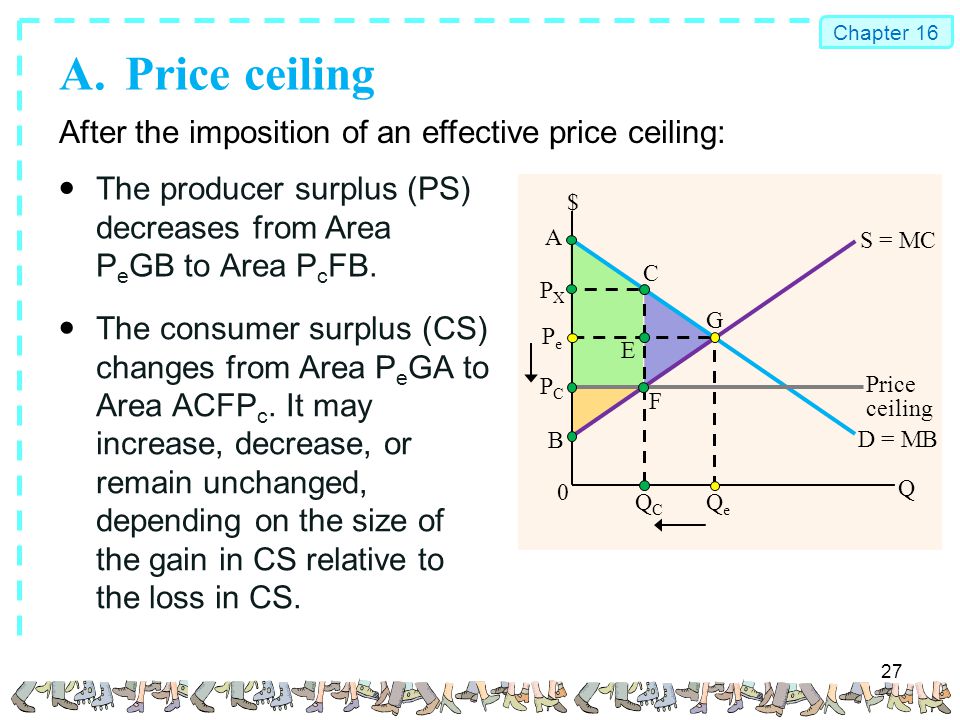
Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low. This is the currently selected item. Rectangles b and c. Change from areas a b e to areas a b c.
Unfortunately it like any price floor creates a surplus. However price floor has some adverse effects on the market. Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers. Price and quantity controls.
Minimum wage and price floors. A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at. How price controls reallocate surplus.
Price helps define consumer surplus but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal or at equilibrium. Fall from areas c d f to area d. Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers. When society or the government feels that the price of a commodity is too low policymakers impose a price floor establishing a minimum price above the market equilibrium.
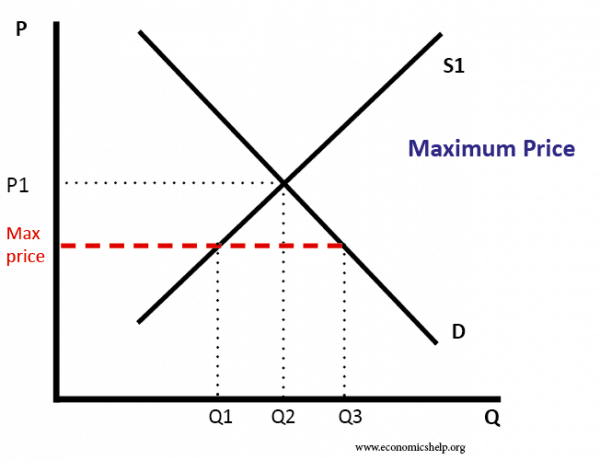
If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy. Fall from areas a b e to area a. A government imposed price control or limit on how high a price is charged for a product. The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
When the price is above the equilibrium the quantity supplied will be greater than the quantity demanded and there will be a surplus. Change from areas c d f to areas b c d. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. Triangles e and f.